Leveraging OCI Runtime Annotations for Kubernetes Tooling
In the Kubernetes ecosystem, several projects are tracing containers using low-level
Linux primitives such as eBPF, fanotify, processes, cgroups to name some projects
we have Inspektor Gadget, lockc,
Falco, etc. Those tools might detect a new
container that has been started on a node, but then they need to determine if the
container is part of a Kubernetes cluster and identify the pod to which it belongs.
One way to get this information is to use Kubernetes API server and filter
based on pod.status.containerStatuses.containerID:
$ kubectl explain pods.status.containerStatuses.containerID
KIND: Pod
VERSION: v1
FIELD: containerID <string>
DESCRIPTION:
Container's ID in the format '<type>://<container_id>'.
But if the tool will be running on Kubernetes worker nodes one must be careful since:
- There can be performance implications since for each container we will need to do unnecessary roundtrips to get the metadata from the API server.
- The API server might not be aware of the
containerIDyet because we might be querying a bit too early in the life cycle of a pod.
In this blog, we will look at the alternatives for the above approach and introduce a Golang package that uses it.
The Container Stack in Kubernetes
In Kubernetes, a component called kubelet takes care of talking to container runtimes to handle container workloads.
kubelet uses Container Runtime Interface (CRI) to manage containers, a simplistic flow of their interaction is show below:
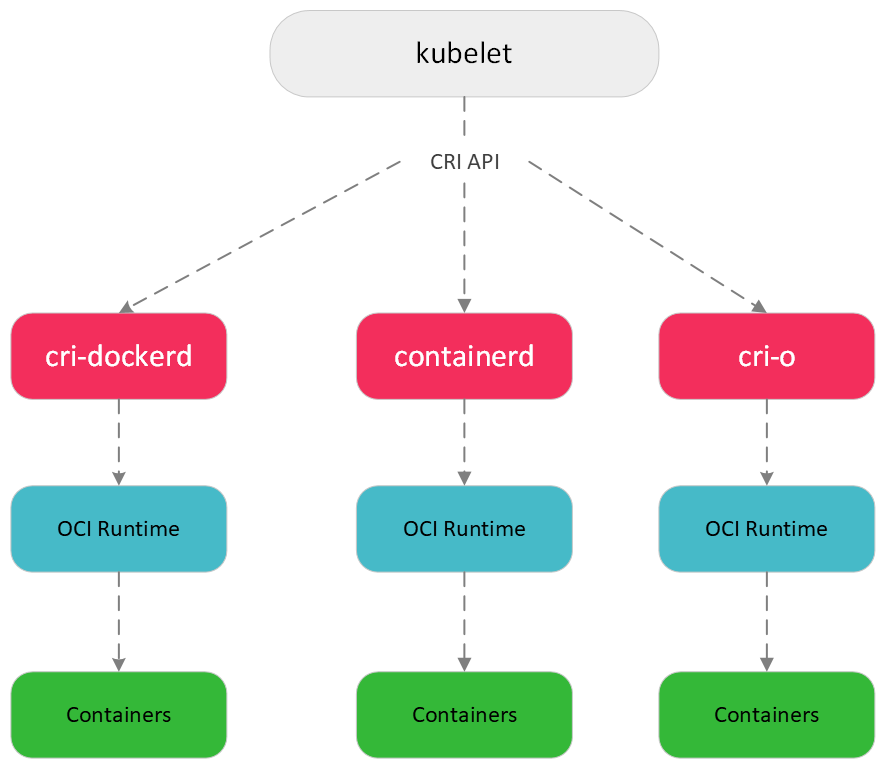
While interacting with container runtimes kubelet also passes metadata that can be useful for tools and container runtimes.
This metadata is shared as part of the CRI API e.g. RunPodSandbox.
The following message shows some metadata passed to container runtimes by kubelet as part of PodSandboxConfig:
// PodSandboxMetadata holds all necessary information for building the sandbox name.
// The container runtime is encouraged to expose the metadata associated with the
// PodSandbox in its user interface for better user experience. For example,
// the runtime can construct a unique PodSandboxName based on the metadata.
message PodSandboxMetadata {
// Pod name of the sandbox. Same as the pod name in the Pod ObjectMeta.
string name = 1;
// Pod UID of the sandbox. Same as the pod UID in the Pod ObjectMeta.
string uid = 2;
// Pod namespace of the sandbox. Same as the pod namespace in the Pod ObjectMeta.
string namespace = 3;
// Attempt number of creating the sandbox. Default: 0.
uint32 attempt = 4;
}
It is up to the container runtime to decide how and what information it wants to expose.
Container Runtimes and OCI Runtime Annotations
Both containerd and cri-o have mechanisms to store pod information locally on the node. They use OCI (Open Container Initiative) runtime annotation field,
which can be used to store arbitrary data. These annotations are available via config.json in bundle directory
for the container as governed by OCI runtime specification.
containerd
$ jq .annotations /run/containerd/io.containerd.runtime.v2.task/k8s.io/7be7ca56452ce0f69575654683e3b8cdc61d8898d06caf92fbf5ffffcd856bd7/config.json
{
"io.kubernetes.cri.container-name": "coredns",
"io.kubernetes.cri.container-type": "container",
"io.kubernetes.cri.image-name": "k8s.gcr.io/coredns/coredns:v1.8.6",
"io.kubernetes.cri.sandbox-id": "2f8ce2bd696584bcc7d7c107135a38354d6766bc7ea7dd137bb4acfc92592268",
"io.kubernetes.cri.sandbox-name": "coredns-6d4b75cb6d-w4b72",
"io.kubernetes.cri.sandbox-namespace": "kube-system"
"io.kubernetes.cri.sanbox-uid": "01b4b887-7635-4346-9c20-58a294bbb034"
}
cri-o
$ jq .annotations /run/containers/storage/overlay-containers/438e2ba9d5970597608a7df68ae72f6085a1460f976f964ed5f369c793eaa4fe/userdata/config.json
{
"io.container.manager": "cri-o",
"io.kubernetes.container.name": "coredns",
"io.kubernetes.cri-o.ContainerID": "438e2ba9d5970597608a7df68ae72f6085a1460f976f964ed5f369c793eaa4fe",
"io.kubernetes.cri-o.ContainerType": "container",
"io.kubernetes.cri-o.ImageName": "k8s.gcr.io/coredns/coredns:v1.8.6",
"io.kubernetes.cri-o.SandboxID": "500027715b8ab8cdb7871c0894b8a7d3eea199c7a8f458351952f44a6ad6cc14",
"io.kubernetes.pod.name": "coredns-6d4b75cb6d-4mtdm",
"io.kubernetes.pod.namespace": "kube-system",
"io.kubernetes.pod.uid": "5b5e07db-f1b9-4530-81ef-b7d04d66b83e"
...
...
}
The main thing to notice here is the runtimes are using different annotations for the same information e.g. io.kubernetes.cri.sanbox-uid vs io.kubernetes.pod.uid.
Also, in terms of support, cri-o has supported Kubernetes annotations for the past few releases but we upstreamed the changes related to pod uid
in containerd recently and it should be available from v1.6.11 onwards. You can have a look at sandbox_run_linux.go (cri-o) and container_create_linux.go (containerd) for more information.
Inspektor Gadget
Inspektor Gadget is a collection of tools to debug and inspect Kubernetes resources and applications. To trace all the events from newly created containers Inspektor Gadget needs to detect new containers and inject Kubernetes metadata for the generated events:
$ kubectl gadget trace open -n kube-system -c coredns
NODE NAMESPACE POD CONTAINER PID COMM FD ERR PATH
minikube-docker kube-system coredns-6d4b75cb6d-kcxd4 coredns 337091 coredns 11 0 /etc/hosts
minikube-docker kube-system coredns-6d4b75cb6d-kcxd4 coredns 337091 coredns 11 0 /etc/coredns/Corefile
Apart from performance issues and limitations mentioned above of talking to the API server, one idea would be to call container runtimes for
additional metadata. This approach has its own limitations since to trace the first ever event from the container it is crucial to have container
metadata on hand before the container even starts. While implementing support for cri-o, we realized that we could only query cri-o container over CRI API
once it was in a running state which is too late for us.
But given that Inspektor Gadget uses runcfanotifyto detect these
containers, it already has access to the bundle directory and hence
config.json for each newly created container. The overall flow to get the annotations is as follows:
- RuncNotifier watches for
runc createevents. It also registers acallbackfor these events. - Upon receiving a
runc createevent, we parsecmdlineto obtainbundle directory(--bundle). - We unmarshall the
config.jsonfrom bundle directory and invokecallbackwith ContainerEvent. - The ContainerEvent holds the OCI runtime spec and hence OCI annotations making them available down the stack without any additional GRPC calls.
This solves the issue of getting the annotations, but we still need to handle the case of how each runtime has different annotations for the same information. To handle this, we created the oci-annotations package to resolve the annotations for different container runtimes as:
resolver, err := ociannotations.NewResolverFromAnnotations(container.OciConfig.Annotations)
// ignore if annotations aren't supported for runtime e.g. docker
if err != nil {
log.Debugf("OCIConfig enricher: failed to initialize annotation resolver: %s", err)
return true
}
// enrich the container
container.Runtime = resolver.Runtime()
if name := resolver.ContainerName(container.OciConfig.Annotations); name != "" {
container.Name = name
}
if podName := resolver.PodName(container.OciConfig.Annotations); podName != "" {
container.Podname = podName
}
if podNamespace := resolver.PodNamespace(container.OciConfig.Annotations); podNamespace != "" {
container.Namespace = podNamespace
}
if podUID := resolver.PodUID(container.OciConfig.Annotations); podUID != "" {
container.PodUID = podUID
}
The information is stored in the container-collection via RuncNotifier callback
and added to each trace event generated by a container simplifying the process of adding Kubernetes context in Inspektor Gadget.
Conclusion
In this blog, we went over a particular use case of how one can utilize OCI runtime annotation for their use case.
The idea itself is interesting and can be expanded to downstream more information from kubelet to container runtimes.
We would like to thank the containerd community for the quick reviews and releasing our changes in the stable version.
Finally, please feel free to use oci-annotaions package for your use case and provide us with feedback in case it can be used to handle more information.